Understanding T4 Syndrome: Signs, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies

In the realm of health and medical sciences, understanding complex syndromes such as T4 syndrome is vital for providing effective care and improving patient outcomes. This comprehensive guide delves into the signs and symptoms of T4 syndrome, offering valuable insights for healthcare professionals, chiropractors, and individuals seeking clarity about this condition.
What Is T4 Syndrome? An Overview
T4 syndrome is a neuro-musculoskeletal condition characterized by specific clinical features predominantly affecting the upper back, shoulders, and arms. Named after the thoracic vertebrae involved, particularly the fourth thoracic vertebra (T4), this syndrome manifests through a combination of neurological, muscular, and orthopedic symptoms that often mimic other musculoskeletal disorders.
Etiology and Pathophysiology
The development of T4 syndrome is linked primarily to prolonged poor posture, repetitive strain, trauma, or minor injuries to the thoracic spine. These factors lead to joint dysfunction, nerve irritation, and muscular imbalances around the T4 vertebrae. The resulting nerve sensitization can induce a cascade of symptoms involving the upper limbs and chest, often complicating diagnosis.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of T4 Syndrome
Understanding the detailed signs and symptoms associated with T4 syndrome is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment intervention. The following sections outline the most common clinical features that alert healthcare providers and individuals to the presence of this syndrome.
Primary Signs and Symptoms of T4 Syndrome
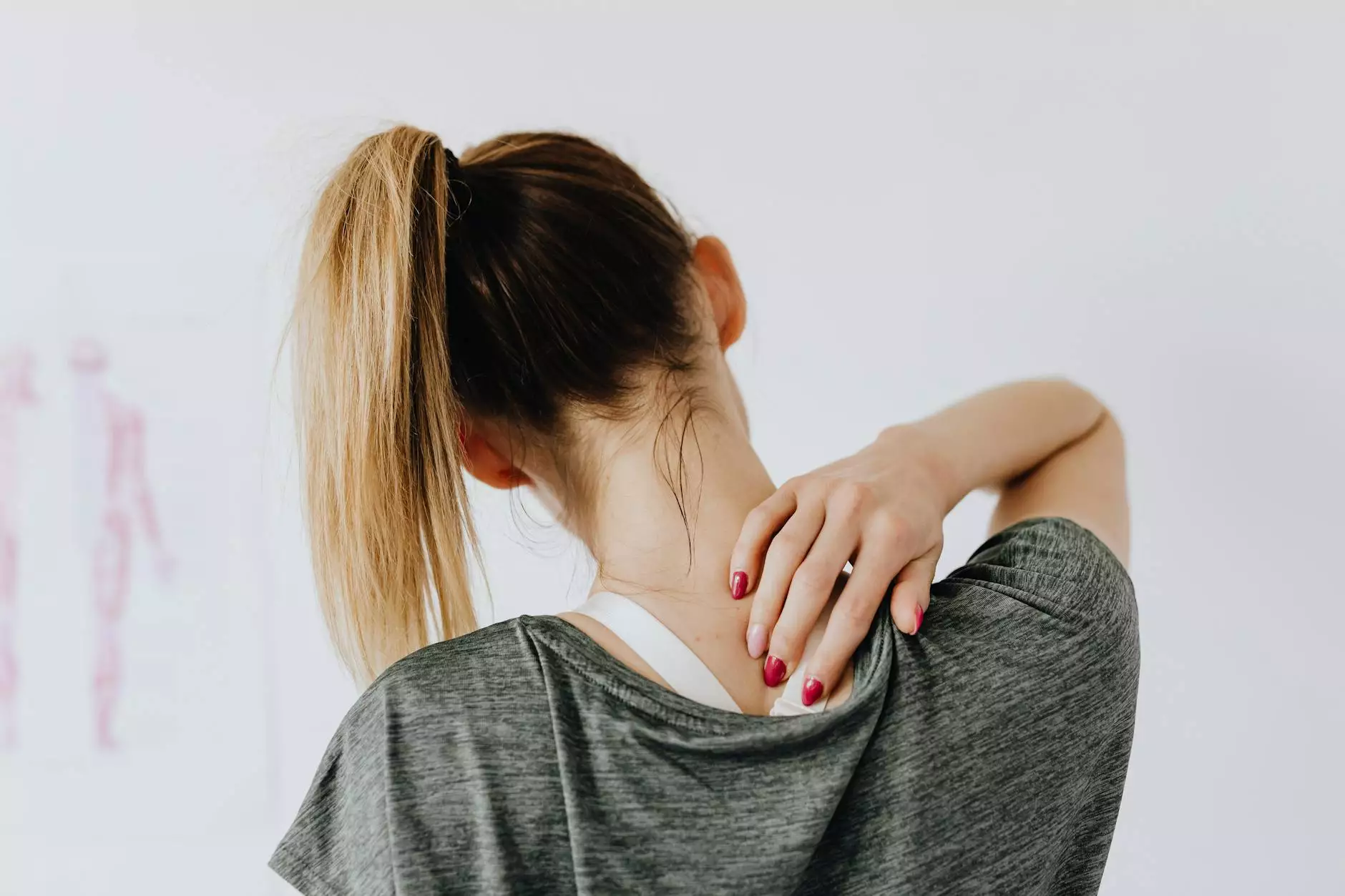
- Upper back pain: Persistent dull or aching pain localized around the mid-back region, often centered at the T4 level.
- Shoulder discomfort: Pain or tenderness in the shoulder girdle, sometimes radiating to the scapula or neck.
- Arm pain and numbness: Often described as a tingling, numb, or 'pins and needles' sensation extending down the arm, frequently affecting the lateral aspect of the forearm and hand.
- Cold sensations in the upper limbs: A distinctive symptom where affected individuals report a feeling of coldness or numbness, suggesting sympathetic nerve involvement.
- Weakness in the upper extremities: Weakness in grip strength or forearm muscles may occur, indicating neurological involvement.
- Referred pain: Pain may be perceived in areas outside the immediate region of the thoracic spine, such as the chest, neck, or jaw.
- Postural aggravation: Symptoms often worsen with sustained poor posture or repetitive movements, such as typing or using a mobile device.
Additional Clinical Features
Besides the primary symptoms, various other signs may develop, particularly if the syndrome remains untreated:
- Reduced shoulder mobility: Stiffness and limited range of motion in shoulder movements.
- Muscle tightness: Increased tension in shoulder, neck, and upper back muscles, particularly the trapezius and rhomboids.
- Palpable tenderness: Tenderness upon palpation of the thoracic spine or surrounding musculature.
- Sleep disturbances: Discomfort or pain that worsens at night, impacting sleep quality.
Understanding the Role of Diagnosis in T4 Syndrome
Diagnosing T4 syndrome requires careful clinical evaluation, including a detailed health history, physical examinations, and sometimes imaging studies. Healthcare providers, including chiropractors and medical practitioners, typically look for the hallmark features outlined above and rule out other conditions such as herniated discs, rotator cuff injuries, or cardiac issues.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
- Physical Examination: Assess range of motion, palpate for tenderness, and evaluate neurological reflexes and muscle strength.
- Postural Analysis: Identify poor postural habits contributing to symptom aggravation.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be employed to rule out structural abnormalities or spinal degenerative changes.
- Neurological Testing: Nerve conduction studies or EMG may be conducted to assess nerve involvement and rule out other neuropathies.
Effective Treatment Strategies for T4 Syndrome
Addressing T4 syndrome involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual's specific presentation and severity. The goals of therapy are to alleviate pain, restore mobility, correct postural issues, and resolve nerve irritation.
Chiropractic Care and Manual Therapy
Chiropractors play a pivotal role in managing T4 syndrome through targeted spinal adjustments, mobilization techniques, and soft tissue therapy. Techniques focus on restoring proper alignment to reduce nerve compression and improve blood flow. Soft tissue massage and trigger point therapy can alleviate muscular tension and improve mobility.
Physical Therapy and Postural Reeducation
Physical therapy interventions aim to strengthen supportive musculature, stretch tight muscles, and promote optimal ergonomics. Postural correction exercises and stabilization routines are essential to prevent recurrence.
Medications and Pain Management
For acute pain relief, NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, or spinal injections may be utilized under medical supervision. However, these are adjuncts to more definitive physical interventions.
Lifestyle Modifications and Preventative Measures
- Maintaining ergonomic workspace setups
- Engaging in regular stretching and strengthening exercises
- Practicing good posture during daily activities
- Avoiding prolonged static positions that stress the upper back
How to Differentiate T4 Syndrome from Similar Conditions
While T4 syndrome shares symptoms with other musculoskeletal and neurological disorders, specific differentiating factors include:
- Referred pain patterns: T4 syndrome often has pain referral zones aligned with the T4 dermatome and myotome.
- Sympathetic features: Cold sensations and vasomotor changes are more characteristic of T4 syndrome than other conditions.
- Postural triggers: Symptoms exacerbate with specific postural positions unique to T4 involvement.
The Importance of Early Intervention and Ongoing Management
Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve prognosis, prevent chronic pain, and reduce the risk of neurological deficits. Regular follow-up, lifestyle adjustments, and targeted therapy are essential components of long-term management.
Conclusion: Empowering Patients and Healthcare Providers
Understanding the signs and symptoms of T4 syndrome is paramount for effective clinical outcomes. By recognizing key symptoms such as upper back pain, shoulder discomfort, arm numbness, and temperature changes, healthcare providers—including chiropractors and medical practitioners—can facilitate early diagnosis and start appropriate treatment. Ensuring that individuals adopt healthy postural habits and partake in proactive therapies can dramatically improve their quality of life.
At iaom-us.com, we are dedicated to providing education, expert chiropractic care, and innovative health solutions to help you understand and manage conditions like T4 syndrome effectively. Prioritize your health today and seek professional guidance for comprehensive care tailored to your needs.
t4 syndrome signs and symptoms