Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain: Understanding, Causes, and Treatments
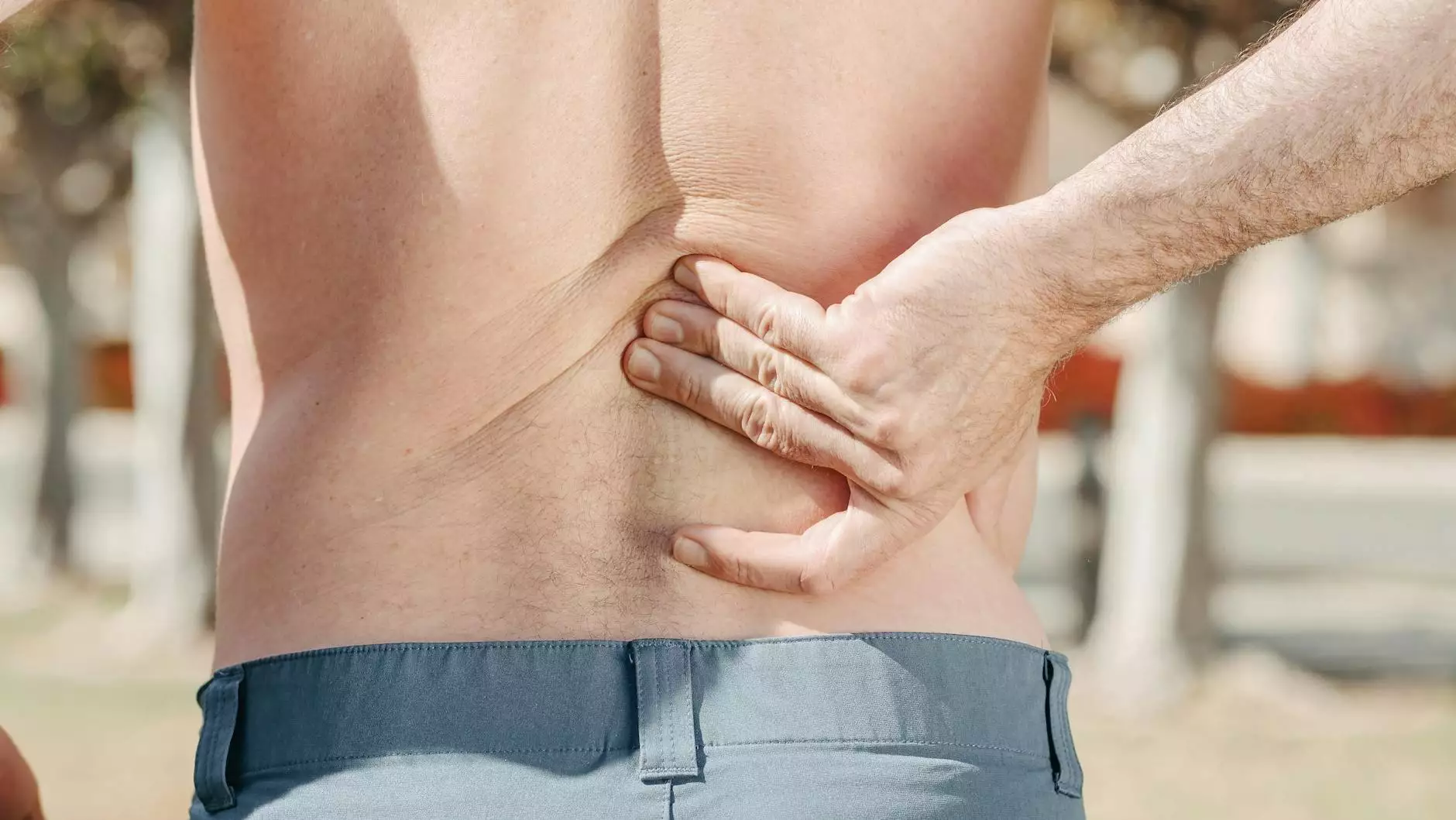
Bilateral thoracic back pain is a condition that affects many individuals, leading to discomfort and affecting daily activities. This article dives deeply into understanding the intricacies of this condition, including the potential causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and the role of healthcare professionals, particularly chiropractors, in managing back pain. By exploring this topic thoroughly, our goal is to equip you with the knowledge required to deal with this issue effectively.
What is Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain?
Bilateral thoracic back pain refers to pain that occurs on both sides of the thoracic region of the spine. This region extends from the base of the neck to the lower back, encompassing 12 thoracic vertebrae. Individuals suffering from this condition may experience pain that can be sharp, dull, or throbbing in nature, significantly impacting their quality of life and mobility.
Common Causes of Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Understanding the underlying causes of bilateral thoracic back pain is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some common reasons for this condition:
- Poor Posture: Slouching or sitting hunched over can place excessive strain on the thoracic spine.
- Muscle Strain: Overexertion during physical activities can cause muscle strain or injury, leading to pain.
- Injuries: Sports injuries, falls, or accidents can result in pain in the thoracic area.
- Herniated Discs: A herniated disc in the thoracic spine can put pressure on spinal nerves, causing pain.
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis can lead to inflammation and pain in the thoracic region.
- Stress and Anxiety: Muscle tension associated with stress can contribute to pain and discomfort.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Individuals experiencing bilateral thoracic back pain may exhibit various symptoms, which can include:
- Sharp or Dull Pain: Varying degrees of discomfort may be experienced.
- Radiating Pain: Pain may extend to the shoulders, arms, or chest.
- Stiffness: Reduced flexibility or difficulty in movement in the thoracic region.
- Numbness or Tingling: Some may experience nerve-related symptoms due to compression.
Diagnosing Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Proper diagnosis is essential in addressing bilateral thoracic back pain effectively. Healthcare professionals, including chiropractors, will typically conduct a thorough medical history review and physical examination. Additional diagnostic tools include:
- X-Rays: To visualize the bony structures of the thoracic spine.
- MRIs: To assess soft tissue structures, discs, and nerves.
- CT Scans: For a more detailed view of the spine.
Treatment Options for Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Treating bilateral thoracic back pain typically involves a multifaceted approach. The treatment plan may include:
1. Chiropractic Care
Chiropractors specialize in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal disorders. They utilize various techniques, including spinal manipulation, to help restore proper alignment and alleviate pain. Regular chiropractic adjustments can enhance mobility and promote overall spinal health.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapists design personalized rehabilitation programs aimed at strengthening the muscles surrounding the thoracic spine, improving posture, and increasing flexibility. Techniques may include:
- Stretching Exercises: To alleviate tightness and improve range of motion.
- Strengthening Exercises: To enhance support for the spinal structures.
- Posture Training: To correct posture and reduce strain.
3. Medication
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage mild to moderate pain. In some cases, physician-prescribed medication may be necessary for inflammation or severe pain.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly impact back health. Suggestions include:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Reducing excess weight can lessen the strain on the back.
- Staying Active: Engaging in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling can enhance overall health.
- Practicing Good Posture: Being mindful of posture while sitting, standing, or lifting can prevent further injury.
5. Alternative Treatments
Many individuals find relief through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or yoga. These practices can help reduce tension, promote relaxation, and improve flexibility.
Preventing Bilateral Thoracic Back Pain
Preventive measures can be effective in minimizing the risk of developing bilateral thoracic back pain. These include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in strength and flexibility exercises can support spinal health.
- Avoiding Prolonged Sitting: Taking regular breaks during desk work can reduce strain.
- Using Ergonomic Furniture: Investing in ergonomic chairs and desks can promote better posture.
Conclusion
In summary, bilateral thoracic back pain can arise from various causes, impacting individuals significantly. Understanding the condition, recognizing symptoms, and knowing available treatments are vital steps in managing pain. By engaging with healthcare professionals, particularly chiropractors, and implementing lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively reduce discomfort and improve their quality of life.
For more information on managing thoracic back pain and finding a qualified chiropractor, visit iaom-us.com.